Embarking on a journey of thermal exploration, the student exploration heat transfer by conduction answer key unlocks the mysteries of heat transfer through direct contact. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of conduction, empowering students with a profound understanding of how heat propagates through matter, shaping our everyday experiences and driving countless industrial processes.
Delving into the heart of conduction heat transfer, this exploration unveils its fundamental principles, unveils its applications across diverse fields, and illuminates advanced concepts that govern its efficiency. Prepare to immerse yourself in a world of thermal energy transfer, where heat flows effortlessly from one object to another, leaving an indelible mark on our physical world.
1. Definition of Conduction Heat Transfer
Conduction heat transfer is the transfer of heat energy between objects or within an object due to a temperature difference. It occurs when molecules or atoms in contact with each other collide, transferring thermal energy from higher-energy molecules to lower-energy molecules.
In everyday life, conduction heat transfer can be observed in various scenarios, such as when you touch a hot stove or when heat travels through a metal spoon placed in a hot soup.
The rate of conduction heat transfer is influenced by several factors, including the temperature difference between the objects, the surface area in contact, the material’s thermal conductivity, and the thickness of the material.
2. Student Exploration Activities
Design an Experiment to Demonstrate Conduction Heat Transfer
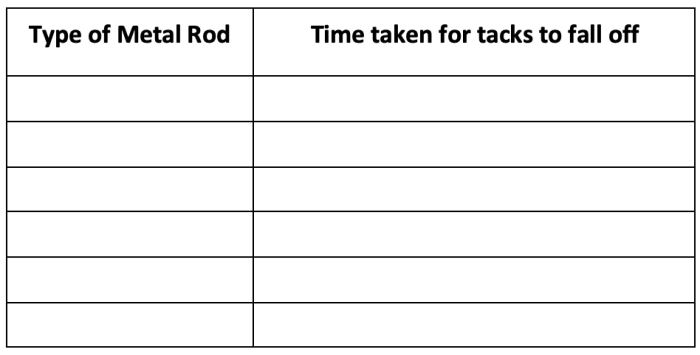
To demonstrate conduction heat transfer, students can conduct an experiment using two metal rods of different lengths and a heat source. By measuring the temperature change at different points along the rods over time, students can observe the transfer of heat energy through conduction.
Create a Table to Record the Results of the Experiment
Students should create a table to record the temperature readings at specific time intervals. This data will help them analyze the rate of heat transfer and identify the factors that affect it.
Analyze the Data and Draw Conclusions about Conduction Heat Transfer
By analyzing the data collected, students can draw conclusions about the rate of conduction heat transfer and how it is affected by variables such as temperature difference, surface area, and material properties.
3. Real-World Applications of Conduction Heat Transfer: Student Exploration Heat Transfer By Conduction Answer Key
Conduction heat transfer has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Heating and cooling systems:Conduction is used in heat exchangers, radiators, and air conditioners to transfer heat from one fluid to another.
- Electronics:Heat sinks are used in electronic devices to dissipate heat away from sensitive components.
- Manufacturing:Conduction is utilized in processes such as forging, welding, and casting to transfer heat into or out of materials.
4. Advanced Concepts in Conduction Heat Transfer
Explain the Concept of Thermal Conductivity
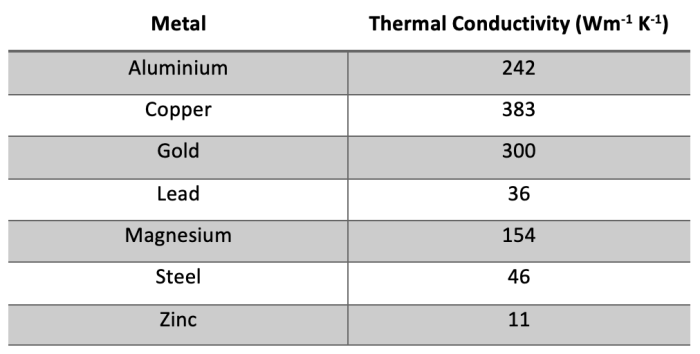
Thermal conductivity is a material property that measures its ability to conduct heat. It is defined as the amount of heat energy transferred per unit time, per unit area, per unit temperature gradient. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals, transfer heat more efficiently than materials with low thermal conductivity, such as plastics.
Provide Examples of Materials with High and Low Thermal Conductivity, Student exploration heat transfer by conduction answer key
- High thermal conductivity:Copper, aluminum, silver, steel
- Low thermal conductivity:Wood, plastic, rubber, glass
Discuss the Role of Thermal Conductivity in Heat Transfer Applications
Thermal conductivity plays a crucial role in heat transfer applications. Materials with high thermal conductivity are used in situations where efficient heat transfer is desired, while materials with low thermal conductivity are used for insulation purposes.
Expert Answers
What is the primary mechanism of heat transfer in conduction?
Conduction heat transfer occurs when heat flows through direct contact between two objects or substances, without the involvement of any intermediate fluid.
Can you provide an example of conduction heat transfer in everyday life?
When you touch a hot stove, heat from the stovetop is transferred to your hand through conduction, causing a sensation of warmth.
What factors influence the rate of conduction heat transfer?
The rate of conduction heat transfer is primarily determined by the temperature difference between the objects, the cross-sectional area of contact, the distance between the objects, and the thermal conductivity of the materials involved.