The combustion of ethane c2h6 produces carbon dioxide and steam – The combustion of ethane (C2H6) is a fundamental chemical process with significant implications in energy production, environmental chemistry, and industrial applications. This reaction, which yields carbon dioxide and steam as its primary products, offers a unique lens through which to explore the principles of thermodynamics, kinetics, and environmental sustainability.
As we delve into the intricacies of ethane combustion, we will uncover its exothermic nature, analyze the factors influencing its reaction rate, and assess its environmental impact. Moreover, we will explore the industrial applications of ethane as a fuel, emphasizing the importance of combustion efficiency and safety considerations.
1. Introduction
Combustion is a chemical process that involves the rapid reaction of a substance with oxygen, releasing heat and light. The combustion of ethane (C2H6), a hydrocarbon, is a fundamental reaction in chemistry.
The chemical equation for the combustion of ethane is:
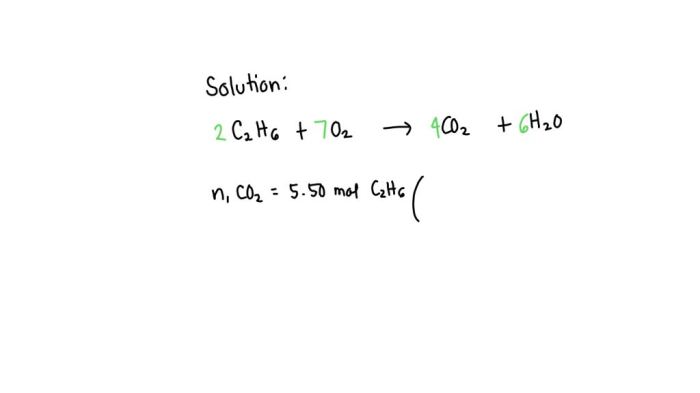
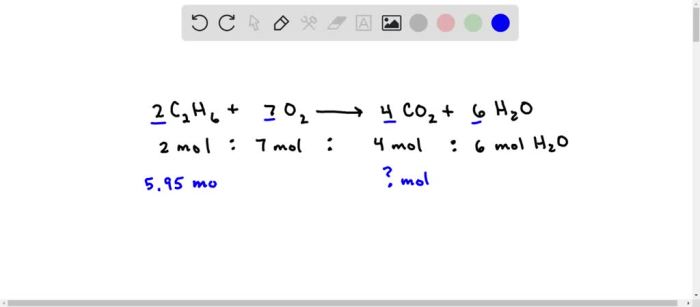
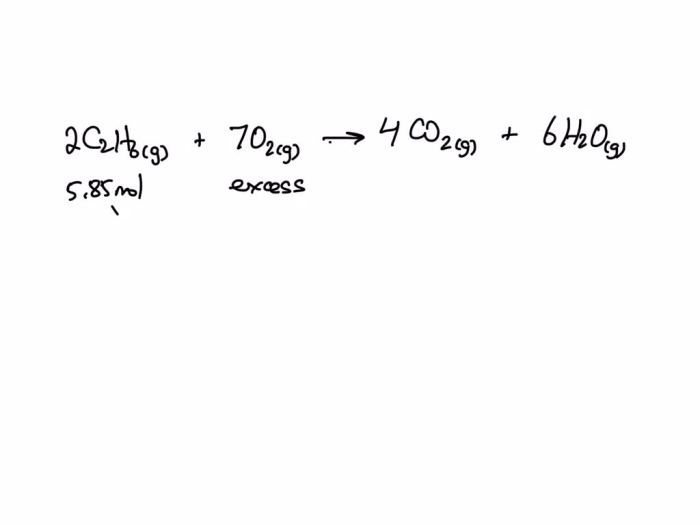
C2H6 + 7O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
The products of combustion are carbon dioxide (CO2) and steam (H2O).
2. Thermodynamics of Combustion
The combustion of ethane is an exothermic reaction, meaning that it releases heat. The enthalpy change (ΔH) for the combustion of ethane is -1560 kJ/mol.
The heat released during combustion depends on several factors, including the type of fuel, the amount of oxygen available, and the temperature.
3. Kinetics of Combustion: The Combustion Of Ethane C2h6 Produces Carbon Dioxide And Steam
The combustion of ethane occurs in several stages, including initiation, propagation, and termination.
The rate-limiting step in the combustion of ethane is the reaction between ethane and oxygen to form a free radical. The rate of this reaction is affected by temperature, pressure, and concentration.
4. Environmental Implications

The combustion of ethane releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
Strategies for reducing carbon dioxide emissions from ethane combustion include using more efficient combustion technologies and capturing and storing carbon dioxide.
5. Industrial Applications
Ethane is used as a fuel in various industries, including power generation, heating, and transportation.
Combustion efficiency is important in industrial processes to maximize energy output and minimize emissions.
Safety considerations associated with ethane combustion include the risk of explosions and fires.
FAQ Insights
What is the chemical equation for the combustion of ethane?
2C2H6 + 7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O
Why is the combustion of ethane an exothermic reaction?
The combustion of ethane releases heat because the products (carbon dioxide and water) are more stable than the reactants (ethane and oxygen).
What are the environmental implications of ethane combustion?
The combustion of ethane releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.