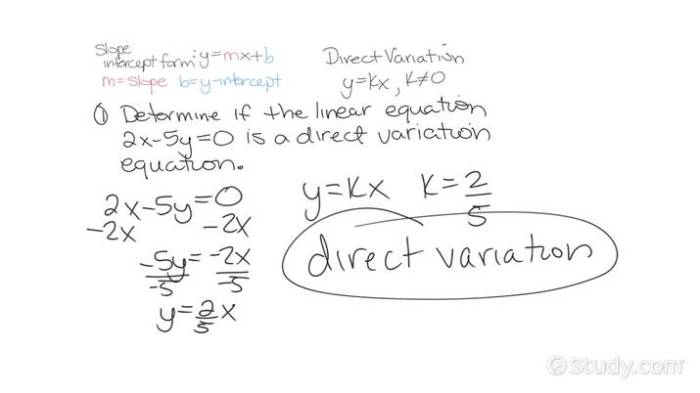Welcome to the ultimate resource for Direct Variation Common Core Algebra 2 Homework Answers. This comprehensive guide is meticulously crafted to provide a thorough understanding of direct variation, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to conquer any homework assignment with confidence.
Embark on a journey of mathematical exploration as we delve into the concept of direct variation, uncover its applications in real-world scenarios, and master the art of solving direct variation problems. Our team of experts has meticulously curated this guide to empower you with a deep understanding of this fundamental algebraic concept.
Direct Variation
Direct variation is a mathematical relationship between two variables, where the value of one variable is directly proportional to the value of the other variable.
Define Direct Variation, Direct variation common core algebra 2 homework answers
Direct variation occurs when the ratio of the two variables is constant. This means that if one variable increases by a certain factor, the other variable will increase by the same factor.
The equation for direct variation is written as:
y = kx
where:
- y is the dependent variable
- x is the independent variable
- k is the constant of variation
Solve Direct Variation Problems
To solve direct variation problems, you need to find the value of the constant of variation (k). You can do this by using two points on the line of variation.
Once you have the value of k, you can use the equation to find the value of y for any value of x.
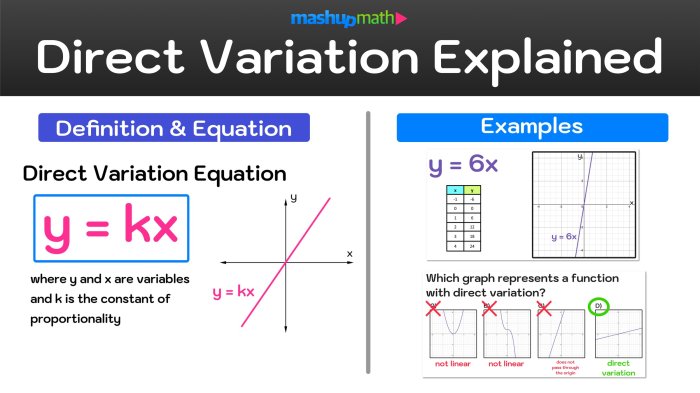
Graph Direct Variation Equations
The graph of a direct variation equation is a straight line that passes through the origin. The slope of the line is equal to the constant of variation.
You can use the slope of the line to find the constant of variation, or you can use the equation to find the slope of the line.
Applications of Direct Variation
Direct variation has many applications in real life. Some examples include:
- The relationship between the distance traveled and the time taken to travel that distance
- The relationship between the volume of a gas and its temperature
- The relationship between the force applied to an object and the acceleration of the object
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems on direct variation:
- A car travels 200 miles in 4 hours. What is the constant of variation?
- The volume of a gas is 10 liters at a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius. What is the volume of the gas at a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius?
- A force of 10 newtons is applied to an object, and the object accelerates at a rate of 2 meters per second squared. What is the mass of the object?
Advanced Topics
In addition to direct variation, there are also other types of variation, such as:
- Inverse variation
- Joint variation
These types of variation are more complex than direct variation, but they can be used to model a wider range of real-world phenomena.
Query Resolution: Direct Variation Common Core Algebra 2 Homework Answers
What is direct variation?
Direct variation is a mathematical relationship between two variables, where one variable changes in direct proportion to the other. This means that as one variable increases, the other variable also increases proportionally.
How do I solve direct variation problems?
To solve direct variation problems, you can use the following formula: y = kx, where y is the dependent variable, x is the independent variable, and k is the constant of variation.
How do I graph direct variation equations?
To graph direct variation equations, you can plot the points (x, y) that satisfy the equation. The graph of a direct variation equation is a straight line that passes through the origin.