Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet Answers PDF: Embark on a journey into the captivating world of nitrogen cycling, a fundamental process that sustains the delicate balance of ecosystems. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate steps, key players, and environmental implications of the nitrogen cycle, providing a thorough understanding for students, educators, and environmental enthusiasts alike.
Unveiling the mysteries of nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification, this worksheet unravels the intricate dance of microorganisms and chemical reactions that transform atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for plants and other organisms. Explore the impact of environmental factors and human activities on the nitrogen cycle, gaining insights into its critical role in agriculture, wastewater treatment, and environmental monitoring.
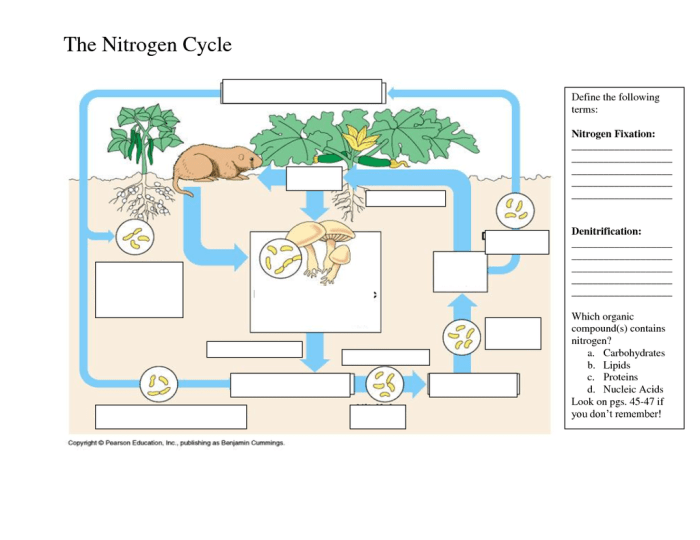
Nitrogen Cycle Basics
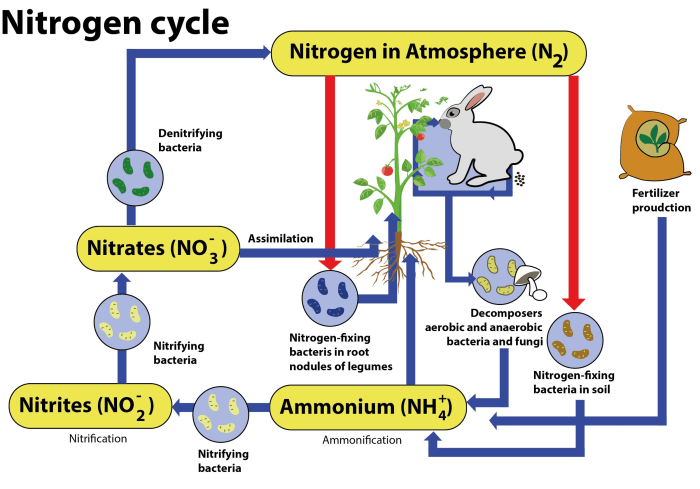
The nitrogen cycle is a fundamental biogeochemical process that ensures the availability of nitrogen in ecosystems. It involves the transformation of nitrogen into various forms, enabling organisms to utilize it for growth and survival.
Bacteria play a crucial role in each step of the nitrogen cycle. They convert nitrogen into usable forms and recycle it back into the environment, making it available for plants and other organisms.
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3). This process is carried out by specialized bacteria known as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which possess the enzyme nitrogenase. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria can be free-living, such as Azotobacter and Clostridium, or symbiotic, forming associations with plants, such as Rhizobium in the roots of legumes.
Steps of the Nitrogen Cycle: Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet Answers Pdf
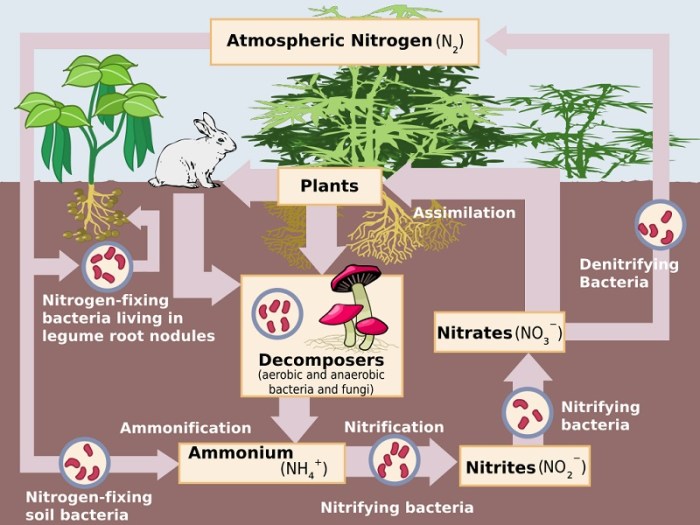
The nitrogen cycle is a complex process that involves the conversion of nitrogen from one form to another. This process is essential for life on Earth, as nitrogen is a key component of proteins, nucleic acids, and other biological molecules.
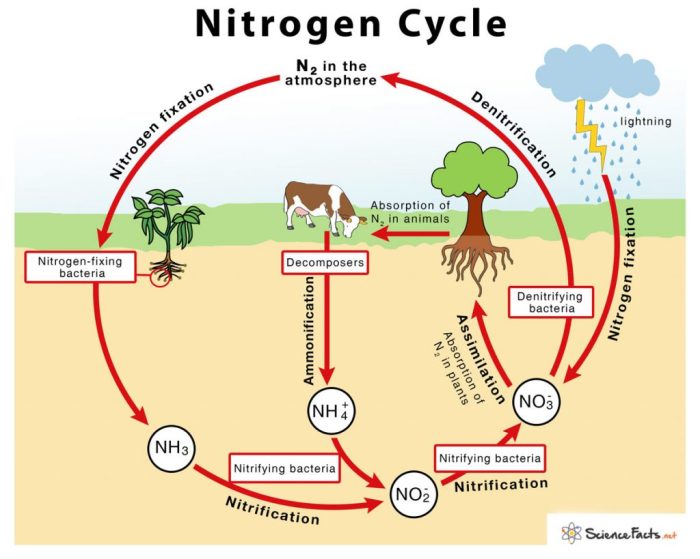
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be used by plants and other organisms. This process is carried out by certain types of bacteria, such as Rhizobiumand Frankia, and by lightning.
When bacteria fix nitrogen, they use an enzyme called nitrogenase to break the triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms in atmospheric nitrogen. This process requires a lot of energy, and it is only carried out by a few types of bacteria.
Lightning can also fix nitrogen. When lightning strikes the ground, it creates a high-temperature plasma that can break the triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms in atmospheric nitrogen.
Nitrification
Nitrification is the process of converting ammonia into nitrates. This process is carried out by two types of bacteria: Nitrosomonasand Nitrobacter.
Nitrosomonasbacteria convert ammonia into nitrite. This process is called nitritation.
Nitrobacterbacteria convert nitrite into nitrate. This process is called nitratation.
Assimilation
Assimilation is the process by which plants and other organisms utilize nitrates. Nitrates are essential for plant growth, as they are used to synthesize proteins and nucleic acids.
Plants absorb nitrates from the soil through their roots. The nitrates are then transported to the leaves, where they are used to synthesize proteins and nucleic acids.
Ammonification, Nitrogen cycle worksheet answers pdf
Ammonification is the process of converting organic nitrogen into ammonia. This process is carried out by decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi.
When decomposers break down organic matter, they release ammonia as a byproduct. This ammonia can then be used by plants and other organisms.
Denitrification
Denitrification is the process of converting nitrates back into atmospheric nitrogen. This process is carried out by denitrifying bacteria, such as Pseudomonasand Bacillus.
Denitrifying bacteria use nitrates as an electron acceptor in the process of respiration. This process releases atmospheric nitrogen as a byproduct.
Factors Affecting the Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is a complex process influenced by various environmental factors and human activities. These factors can impact the activity of bacteria involved in the cycle and disrupt the delicate balance of the system.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors that affect the nitrogen cycle include temperature, pH, and oxygen availability.
- Temperature:Temperature affects the metabolic rates of bacteria. Higher temperatures generally increase the activity of bacteria, while lower temperatures slow it down. This can impact the rates of nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification.
- pH:The pH of the environment can influence the availability of nitrogen to bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria, responsible for converting ammonia to nitrate, prefer neutral to slightly alkaline conditions. Acidic conditions can inhibit their activity, reducing nitrate production.
- Oxygen availability:Oxygen availability plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle. Nitrification is an aerobic process that requires oxygen, while denitrification is an anaerobic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. Changes in oxygen availability can shift the balance between these processes, affecting the overall nitrogen cycle.
Human Activities
Human activities have a significant impact on the nitrogen cycle, particularly through agriculture, industrialization, and pollution.
- Agriculture:Fertilizer application in agriculture can introduce excess nitrogen into the environment. When nitrogen levels exceed plant needs, it can leach into waterways, causing eutrophication and other environmental problems. Additionally, livestock production generates large amounts of nitrogen-rich manure, which can contribute to nutrient runoff and air pollution.
- Industrialization:Industrial processes, such as fossil fuel combustion and manufacturing, release nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. These oxides can contribute to acid rain and smog, which can affect the health of plants and ecosystems.
- Pollution:Wastewater discharge and sewage treatment plants can release nitrogen into aquatic ecosystems. Excess nitrogen can lead to algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and fish kills.
Applications of the Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle plays a crucial role in various fields, including agriculture, wastewater treatment, and environmental monitoring. Understanding the applications of the nitrogen cycle enables us to harness its benefits and mitigate its potential impacts.
Agriculture
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth and crop production. Nitrogen fertilizers, such as urea and ammonium nitrate, are widely used to supplement the natural nitrogen supply in soils. By increasing the availability of nitrogen, fertilizers enhance crop yields and support global food security.However,
excessive or inappropriate fertilizer application can lead to environmental problems. Nitrate leaching can contaminate groundwater and surface water, causing eutrophication and algal blooms. Nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from fertilizer application contribute to climate change and stratospheric ozone depletion. Therefore, it is crucial to manage nitrogen fertilizer application rates and timing to optimize crop production while minimizing environmental impacts.
Wastewater Treatment
The nitrogen cycle plays a vital role in wastewater treatment plants. Biological processes, such as nitrification and denitrification, are employed to remove nitrogen from wastewater. Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia and ammonium ions into nitrite and nitrate, while denitrifying bacteria reduce nitrate and nitrite to nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere.Efficient
nitrogen removal from wastewater prevents eutrophication in receiving water bodies and protects aquatic ecosystems. It also reduces the risk of human health hazards associated with high nitrate levels in drinking water.
Environmental Monitoring
Indicators of the nitrogen cycle, such as nitrate concentrations in water bodies and soil, can provide valuable insights into environmental health. Changes in nitrogen cycling rates can signal ecosystem disturbances, such as pollution, habitat loss, or climate change.Monitoring nitrogen cycle indicators helps scientists assess the health and resilience of ecosystems, identify potential threats, and develop appropriate management strategies to protect and restore environmental quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of nitrogen fixation in the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrogen fixation is the process that converts atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for plants and other organisms. It is a crucial step in the nitrogen cycle as it makes nitrogen available for biological processes.
How does nitrification contribute to the nitrogen cycle?
Nitrification is the process that converts ammonia into nitrates. It is carried out by nitrifying bacteria and is essential for making nitrogen available to plants in a form they can use.
What is the role of denitrification in the nitrogen cycle?
Denitrification is the process that converts nitrates back into atmospheric nitrogen. It is carried out by denitrifying bacteria and completes the nitrogen cycle, returning nitrogen to the atmosphere.